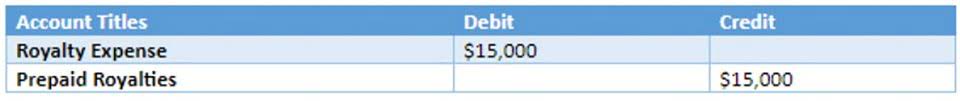
Chapter 6, Cost-Volume-Profit Relationships Video Solutions, Managerial Accounting

You will also learn how to plan for changes in selling price or costs, whether a single product, multiple products, or services are involved. A contribution margin income statement reaches the same bottom-line result as a traditional income statement. While the contribution format sorts costs by whether they are variable or fixed, a traditional income statement separates costs by whether they are tied to production or not. These include the cost of goods sold (COGS) as well as selling, general, and administrative costs (SG&A). The two expense categories may contain both fixed and variable costs, which is why it can be useful to separate them using a contribution format statement. The contribution margin income statement shows fixed and variable components of cost information.
Segment margin
Because expenses are classified as variable or fixed, it is much easier to determine whether a product, service or even segment is profitable or not. Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization (EBITDA) measures a company’s financial health. EBITDA focuses on operating expenses and removes the effects of financing, accounting, and tax decisions. EBIT provides an overall view of the company’s profitability contribution margin income statement level, whereas contribution margin looks at the profitability of each individual service or product. The contribution margin provides the profitability of each individual dish at a restaurant, whereas income would look at the entire restaurant’s overall financial health. Looking at the variable expenses, each skincare product needs ingredients to be formulated, some nice packaging, and a good salesperson on commission.

Calculating Contribution Margin Ratio
- For that, you’ll need a tool that automates data collection, accurately calculates financial insights, and produces customizable reports.
- This step is part of creating a contribution margin statement, which is a type of profit and loss statement.
- Organizational segments can include divisions, individual stores, geographic regions, customers, or product lines.
- This clear division provides insight into cost management strategies and profitability analysis.
Cost volume profit (CVP) analysis can be applied to the whole organization and to particular segments within the organization. Cost volume profit analysis requires a contribution margin format income statement. Cost volume profit analysis is used to make important decisions about selling prices, sales volume, unit variable costs, total fixed costs, and the mix of products sold. Another income statement format, called the contribution margin income statement11 shows the fixed and variable components of cost information.
FAIR VALUE ACCOUNTING: Definition, Example and Advantages
Instead, management must maintain a certain minimum level of staffing in the production area, which does not change with lower production volumes. While the conventional income statement has its uses for external reporting functions, it is not as effective when used for internal reporting purposes. Traditional income statements do not differentiate between fixed and variable costs.
Is gross profit the same as contribution margin?
Variable costs are not consistent and are directly related to the product’s manufacture or sales. They tend to increase as a company scales products and decrease with production. COGS only considers direct materials and labor that go into the finished product, whereas contribution margin also considers indirect costs. A high contribution margin cushions the fall from unexpected costs and dips in sales.

However, the growing trend in many segments of the economy is to convert labor-intensive enterprises (primarily variable costs) to operations heavily dependent on equipment or technology (primarily fixed costs). For example, in retail, many functions that were previously performed by people are now performed by machines or software, such as the self-checkout counters in stores such as Walmart, Costco, and Lowe’s. Since machine and software costs are often depreciated or amortized, these costs tend to be the same or fixed, no matter the level of activity within a given relevant range.
- In addition to companywide income reporting, managers or owners also need to measure the profitability of individual segments within their organizations.
- COGS only considers direct materials and labor that go into the finished product, whereas contribution margin also considers indirect costs.
- Direct materials are often typical variable costs, because you normally use more direct materials when you produce more items.
- Divide the loss by the contribution margin to determine how much to increase sales.
- If variable expenses were $250,000, so you’d have $385 in variable expenses per unit (variable expenses÷units sold).
As a business owner, you’ve likely prepared a traditional income statement, with the usual line items for revenue and expenses, with net income on the bottom line. As the formula above shows, calculating the break-even point requires the contribution margin, which is provided by a contribution margin income statement. Divide the loss by the contribution margin to determine how much to increase sales. The contribution margin and the variable cost can be expressed in the revenue percentage. These are called the contribution margin ratio and variable cost ratio, respectively. This gives a much more detailed financial picture of the business’s operating costs and how well the products perform.

What is Contribution Margin Income Statement?
The contribution margin can then be used to determine how well a particular product or segment is performing. To calculate the contribution margin, you need more detailed financial data to calculate EBIT. Because this figure is usually expressed as a percentage, we’d then divide the contribution margin by the revenue to get the ratio of 0.44. More than 488 units results in a profit, and 486 units or less result in a loss.